Skin pigmentation is a common concern for many people. It refers to the color of your skin, which is mainly determined by a pigment called melanin. Sometimes, changes in skin pigmentation can lead to uneven skin tone, dark spots, or lighter patches. In this blog, we will explore what skin pigmentation is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. We will also share tips to help you care for your skin and prevent pigmentation problems.
What is Skin Pigmentation?
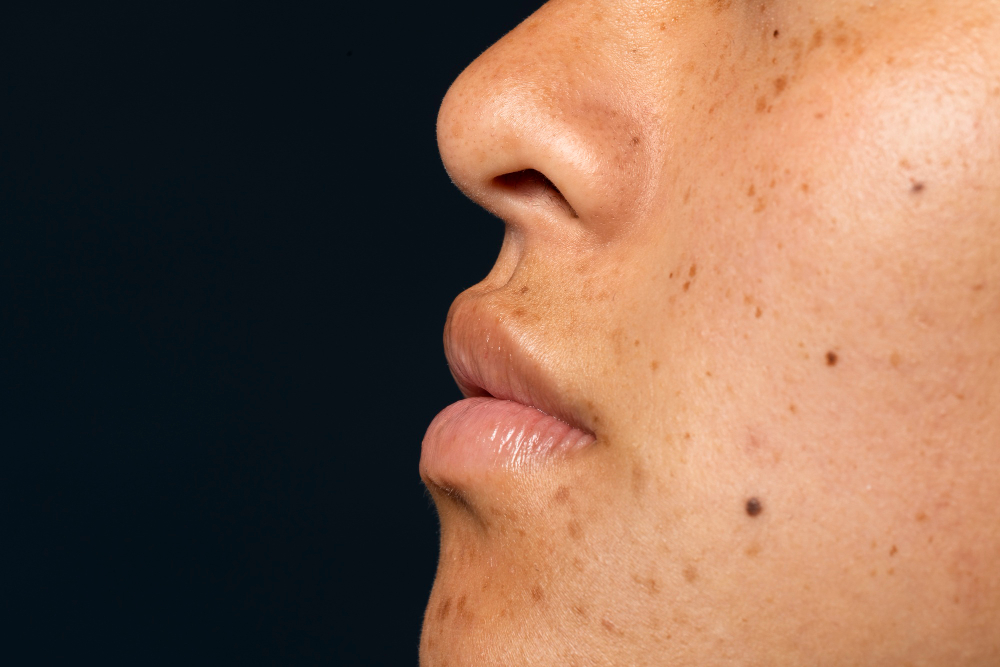
Skin pigmentation is the natural color of your skin. Melanin, made by special cells called melanocytes, gives your skin its color. Everyone has melanin, but the amount and type can vary. This is why people have different skin tones. Sometimes, your skin may develop areas that are darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation) than your normal skin color. These changes can happen for many reasons, including sun exposure, injury, or certain health conditions.
Common Causes of Skin Pigmentation
There are several reasons why skin pigmentation changes. Understanding these causes can help you manage and prevent uneven skin tone or discoloration. For example, some causes are temporary, while others may need medical attention.
Additionally, genetics can play a role in how your skin reacts to these factors.
Symptoms and Types of Pigmentation Disorders
Skin pigmentation disorders can look different from person to person. However, some common symptoms include:
There are several types of pigmentation disorders:
Sometimes, these symptoms can affect self-confidence. But, many treatments are available to help.
How is Skin Pigmentation Diagnosed?
Doctors can often diagnose skin pigmentation disorders by looking at your skin. However, they may ask about your medical history and any recent changes. Sometimes, they use a special light called a Wood’s lamp to see changes in skin color more clearly. In rare cases, a small skin sample (biopsy) may be needed to rule out other conditions. Early diagnosis can help you get the right treatment and prevent further changes.
Treatment Options for Skin Pigmentation
There are many ways to treat skin pigmentation problems. The best option depends on the cause and type of pigmentation. For example, some treatments work better for dark spots, while others help with lighter patches.
It is important to talk to a dermatologist before starting any treatment. Some products can cause side effects or make pigmentation worse if not used correctly. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, sun protection is key during treatment (AAD).
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While not all pigmentation problems can be prevented, you can take steps to protect your skin. For instance, daily habits can make a big difference.
Moreover, regular skin checks can help catch problems early. Simple steps can help you keep your skin healthy and even-toned.
In summary, skin pigmentation changes are common and often treatable. If you have concerns about uneven skin tone, dark spots, or light patches, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on skin pigmentation concerns.